Determine appropriate project methodology/methods and practices
Enablers
- Assess project needs, complexity, and magnitude. (ECO 2.13.1)
- Recommend project execution strategy (e.g., contracting, finance). (ECO 2.13.2)
- Recommend a project methodology/approach (e.g., predictive, agile, hybrid). (ECO 2.13.3)
- Use iterative, incremental practices throughout the project life cycle. (ECO 2.13.4)
Deliverables, and Tools
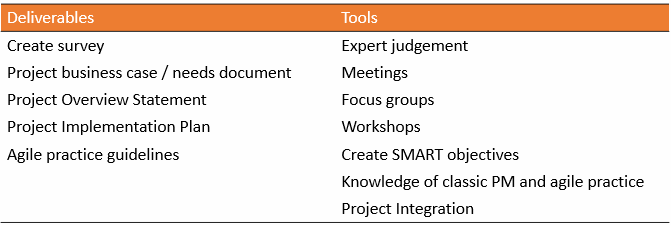
Project Methodologies, Methods, and Practices
Agile: A more modern approach wherein the team works collaboratively with the customer to determine the project needs, quickly building outputs based on those assumptions, getting feedback, and continuing forward or adapting as much as needed.
Predictive / Plan Driven: A more traditional approach wherein as much as possible, the project needs, requirements, and constraints are understood, and plans are developed accordingly. Those plans drive the project forward.
Hybrid: Another option is to incorporate components of both approaches. This may be done by utilizing a particular strategy or technique for a certain need.
Business Case and Business Needs Documents
Business case:
- Documented economic feasibility study
- Used to establish the benefits of project components
- Provides a basis for authorization of further project activities
Business needs documents:
- Provides the high-level deliverables
- Written prior to the formal business case
- Describes what needs to be created and what needs to be performed
Project Implementation Plan
Project deliverables may be delivered all at once at the end of the project.
Project outputs are delivered throughout the project.
When those outputs are delivered is one part of the equation. The other is how the outputs may be:
- Implemented in a new business environment
- Implemented in an existing business environment
- Transitioned into a live environment
- Decommissioning or removing old systems, processes, or materials
- Ensuring training and knowledge transfer is complete or satisfactory
Project Implementation Plans should consider all stakeholders, schedules, risks, budgets, and quality standards.
Assessment of Project Needs, Complexity, and Magnitude
Agile:
Changes are relative easy, and waste is not costly.
Complex environment where end product is not fully known and user feedback is very valuable.
Predictive/Plan Driven:
Changes are expensive due to scrap and waste.
Predictability and coordinated timing is important.
Iterative:
Dynamic requirements and activities are repeated until they are deemed correct.
Hybrid:
There are some costs to changes.
Stakeholders are interested in another method, but not comfortable to fully adopt one
method.
Progressive Elaboration
Progressive elaboration * is the iterative process of increasing the level of detail in a project management plan as greater amounts of information and more accurate estimates become available.
Predictive Life Cycles
A predictive life cycle * is a form of project life cycle in which the project scope, time, and cost are determined in the early phases of the life cycle
Predictive:
- Fixed requirements
- Activities performed once per project
- Single delivery
- Goal: Manage cost
Iterative Life Cycles
An iterative life cycle * is a project life cycle where the project scope is generally determined early in the project life cycle, but time and cost estimates are routinely modified as the project team’s understanding of the product increases.
Iterative:
- Dynamic requirements
- Activities repeated until correct
- Single delivery
- Goal: Correct solution
Incremental Life Cycles
An incremental life cycle * is an adaptive project life cycle in which the deliverable is produced through a series of iterations that successively add functionality within a predetermined time frame. The deliverable contains the necessary and sufficient capability to be considered complete only after the final iteration.
Incremental:
- Dynamic requirements
- Activities performed once per increment
- Frequent small deliveries
- Goal: Speed
Agile Life Cycles
Agile life cycles * are iterative or incremental and also can be referred to as change-driven or adaptive.
Agile:
- Dynamic requirements
- Combines iterative repetition of activities with incremental deliveries
- Goal: Customer value
Hybrid Methodologies
Many organizations are using hybrid methodologies and approaches, which combine some elements from both predictive (waterfall) and adaptive (agile) approaches.
Hybrid:
- Includes adaptive and predictive components
- Shorter, iterative time frames
- High stakeholder involvement
- More in-depth requirements