Lead a team
Enablers
- Set a clear vision and mission. (ECO 1.2.1)
- Support diversity and inclusion. (ECO 1.2.2)
- Value servant leadership. (ECO 1.2.3)
- Determine an appropriate leadership style. (ECO 1.2.4)
- Inspire, motivate, and influence team member/stakeholders. (ECO 1.2.5)
- Analyze team members and stakeholders' influence. (ECO 1.2.6)
- Distinguish various options to lead various team members and stakeholders. (ECO 1.2.7)
- Maintain team. (ECO 1.6.4)
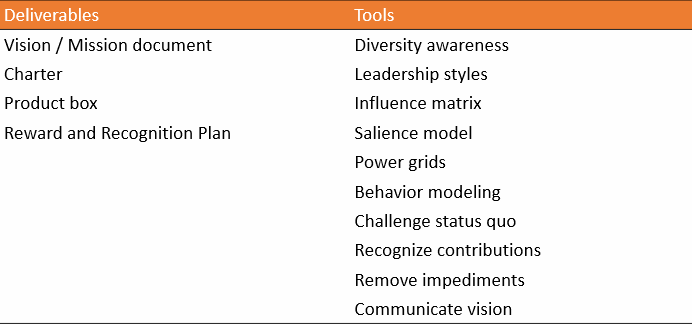
Deliverables, and Tools
Vision and Mission
The project manager is the visionary leader for the project:
- Educating the team and other stakeholders about the value achieved or targeted
- Promoting teamwork and collaboration
- Assisting with project management tools and techniques
- Removing roadblocks
- Articulating the project’s mission
Promoting the project’s mission and value inspires the team to remained focused and feel pride
Diversity Awareness and Cultural Competencies
- Use the leadership approach and style that best suits the situation and the stakeholders.
- Be aware of individual and team aims and working relationships.
- Motivations and working styles of groups and individuals vary based on experiences, age, culture, job roles, and many more influences.
- Projects that include more diverse locations, industries, organizations, stakeholders, working styles, and cultures require communication and openness to build trust.
Leadership Styles
- Strong personal ethics, integrity, and trustworthiness
- Interpersonal skills (communicator, collaborator, motivator)
- Conceptual and analytical skills
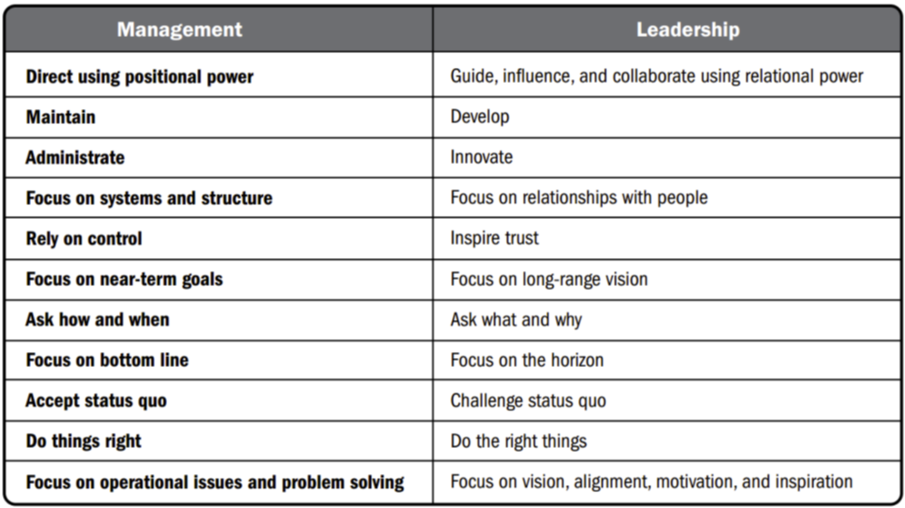
Leadership ≠ Management
Servant Leadership
Servant leadership: A type of leadership commonly used in Agile which encourages the self-definition, self-discovery, and self-awareness of team members by listening, coaching, and providing an environment which allows them to grow.
- Facilitate rather than manage
- Provide coaching and training
- Remove work impediments
- Focus on accomplishments
Challenge the Status Quo
- Past experiences and processes provide guidance but should not dictate the current project.
- Challenging the status quo provides an avenue for new ideas and perspectives.
- Through challenge and introspection, the best approach can be discovered, and complacency and blind acceptance are avoided.
Influence Matrix
Leading a team is based partially on your influence and the influence of the other project stakeholders.
Influence goes in many directions.
The direction is often dictated by roles or titles:
- Upwards (senior management)
- Downwards (team or specialists)
- Outwards (external)
- Sideward (project manager's peers)
The salience classification model can also distinguish influence based on prioritization, urgency, and other aspects.
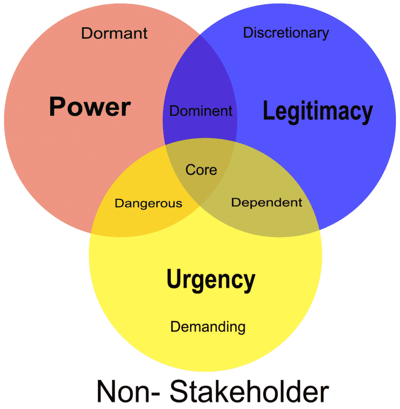
Salience Model
A salience model is a classification model that groups stakeholders on the basis of their level of authority, their immediate needs, and how appropriate their involvement is in terms of the project.
Power Grids
- Power/interest grid: groups stakeholders on the basis of their levels of authority and interest in the project.
- Power/influence grid: a classification model that groups stakeholders on the basis of their levels of authority and involvement in the project.

Team Building
- Project teams perform better when there is increased cohesion and solidarity.
- Good project leadership facilitates the bonding between project team members.
- Facilitating team building activities builds unity, but also builds trust, empathy, and focus on the team over the individual.
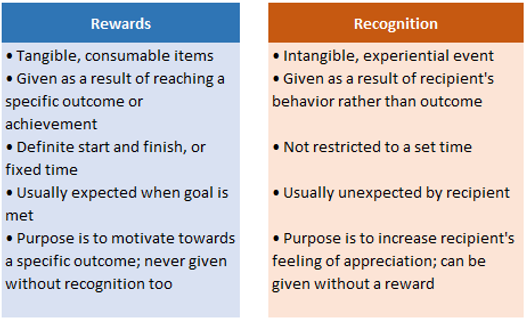
Reward and Recognition Plan
A reward and recognition plan is a formalized way to reinforce performance or behavior.
Guidelines to Manage a Team
- Use emotional intelligence and other style-typing methods to enable you to flex your behavior to a style that works best for each stakeholder.
- Establish good communication among team members, internally and externally.
- Monitor performance of team members on an ongoing basis.
- Manage conflict.
- Establish an issues log to track and assign project issues.