Support organizational change
Enablers
- Assess organizational culture. (ECO 3.4.1)
- Evaluate impact of organizational change to determine required actions. (ECO 3.4.2)
- Evaluate impact of the project to the organization and determine required actions. (ECO 3.4.3)
- Recommend, plan and facilitate the changes.
Deliverables, and Tools
Organizational Cultures and Styles
Every organization develops a unique culture and style that represents its cultural norm and affects how projects are performed. Culture is shaped by people's common experiences such as:
- Shared visions, missions, values, beliefs, and expectations.
- Regulations, policies, methods, and procedures.
- Motivation and reward systems.
- Risk tolerance.
- View of leadership, hierarchy, and authority relationships.
- Code of conduct, work ethic, and work hours.
- Operating environments.
A project manager should understand that cultures have a strong influence on a project's ability to
meet its objectives. He or she also needs to know which individuals in the organization are the
decision makers or influencers and work with them to increase the probability of project success.
Organizational Structures
An organizational structure dictates how the various groups and individuals within the organization interrelate. The organizational structure also affects how much authority the project manager has, as well as the availability of resources and how projects are performed.
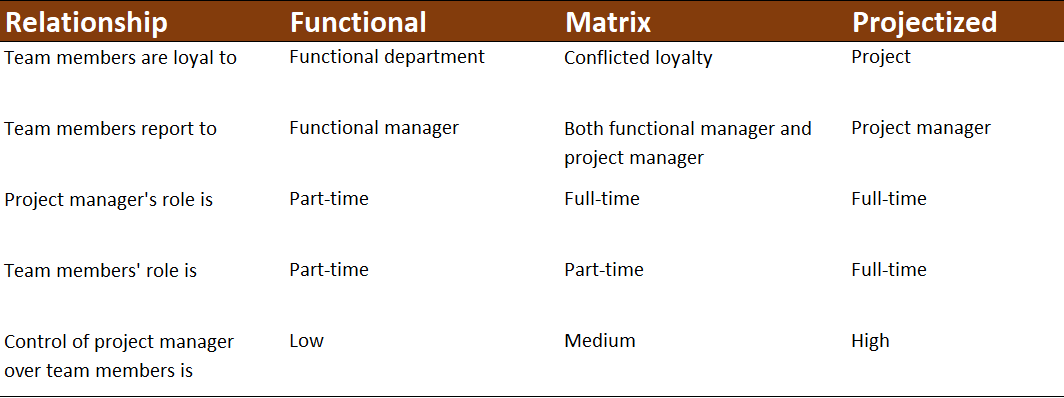
Main structural implementations: functional, matrix, projectized, or composite.
Types of Project Management Organizational Structures

Relative Authority in Organizational Structures
Relative authority refers to the project manager's authority relative to the functional manager’s authority over the project and the project team.
Influences of Organizational Structures on Projects
Project expediter: The project expediter acts primarily as a staff assistant and communications coordinator.
The expediter cannot personally make or enforce decisions.
Project coordinator: This position is similar to the project expediter, except the coordinator has some authority and power to make decisions, and reports to a higher-level manager.
Project Management Office (PMO)
Project management office (PMO) * is a management structure that standardizes the project-related governance processes and facilitates the sharing of resources, methodologies, tools, and techniques.
- Supportive PMOs provide a consultative role to projects by supplying templates, best practices, training access to information, and lessons learned from other projects.
- Controlling PMOs provide support and require compliance through various means. Compliance may involve adopting project management frameworks or methodologies; using specific templates, forms, and tools; or conforming to governance.
- Directive PMOs take control of the projects by directly managing the projects. A relatively small number of PMOs fall into this category.
Organizational Process Assets (OPAs)
Organizational process assets (OPAs) * are plans, processes, policies, procedures, and knowledge bases that are specific to and used by the performing organization.
OPA examples include:
- Guidelines and criteria for aligning project work.
- Specific organizational standards.
- Standard templates for project work.
- Organizational communications requirements.
- Standardized guidelines, work instructions, proposal evaluation criteria, and performance measurement criteria.
- Procedures or requirements for officially closing a project.
Corporate Knowledge Base is a repository for storing and retrieving useful information, including:
- Project files.
- Policies, procedures, and guidelines.
- Human resources documentation.
- Lessons-learned repository.
Enterprise Environmental Factors (EEFs)
Enterprise environmental factors (EEFs) * are the conditions, not under the immediate control of the team, that can influence, constrain, or direct the project, program, or portfolio.
These factors can either support or limit the project management options, act as inputs for planning processes, and have a negative or positive influence on a project outcome.
INTERNAL
Organizational culture, structure, and governance
Geographic distribution of facilities and resources
Infrastructure
Information technology software
Resource availability
Employee capability
EXTERNAL
Marketplace conditions
Social and cultural influences and issues
Legal restrictions
Commercial databases
Academic research
Government or industry standards
Financial considerations
Physical environmental elements
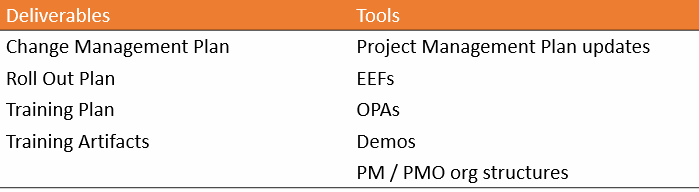
Change Management Plan
The culture of the organization has a direct influence on how the organization manages changes to a project. An organization that exists in a highly regulated environment will tend to have a formal and rigid culture, which will be reflected in how it deals with changes.
Roll Out Plan
Once a change is approved and built, the project manager needs to plan for its successful implementation.
Roll out plans enable the project manager to define the knowledge transfer, training, and readiness activities required to implement the change.
Depending on the size and scope of the change, the affected parties may include:
- Project team and potentially customer and user stakeholders
- Training and support activities
Project Management Plan Updates
Based on the scope of the change, the project management plan may need to undergo substantial updates.
Updates might include:
- Scope
- Timelines
- Work packages
- Individual team member assignments
If the project is agile, impact may be limited to lower-value deliverables being
moved out of scope to make room for the change to be adopted.
Training Plan
Changes to the project plan likely will impact the training plan.
The changes may include:
- The scope of the training and knowledge transfer required
- Changes in roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders
- Changes in the timeline
Training Artifacts
Changes to the plan and deliverable set mean that there will be necessary changes to the training artifacts, which may include:
- Changes to training courseware.
- Changes to lab configurations and exercises.
- Changes to knowledge requirements and potentially to credentials if certification of skills is expected.
- Training updates for the trainers to gain the necessary knowledge transfer they require to deliver the updated training.
Demos
Changes to software solutions may require demonstration of the changed configurations, processes, workflows, and roles and responsibilities.
Demos should be reviewed by the key customer and user stakeholders for feedback to ensure the changes work as intended and do not otherwise impact the workflow of the solution.
Early feedback allows for adaptation while the feedback is still immediately relevant and should have the effect of improving the quality of the change while reducing overall cost and risk.
Guidelines to Recommend, Plan, and Facilitate Changes
- Establish a single way changes are requested with a description of the proposed change, the business value of the change, any risk and risk mitigation recommendations, and the likely cost of the change.
- Ensure that there is a Change Control Board that can assess the change’s cost, risk, and value, other potential impacts to the project, and make recommendations.
- Based on the size of the change and the project’s tolerances, the project manager may approve the change, or may be required to escalate the change for review and approval or disapproval by the project’s governing Board.
- Changes are not made only to hardware, software, or other systems; they affect people, workflows, roles and responsibilities, and the entire organization. Organizational change management best practices should be followed, including building a compelling case for change, getting the buy-in and commitment of key members of the stakeholder group, communicating the change vision, and enabling other stakeholders to engage. Quick wins should be sought, and consolidation and institutionalization of the change should be reinforced.
- Ensure changes are properly aligned and updates to other project artifacts, such as the project plan, training plans, training artifacts, and software configurations or demonstrations.