Integrate project planning activities
Enablers
- Manage and rectify ground rule violations. (ECO 1.12.3)
- Consolidate the project/phase plans. (ECO 2.9.1)
- Assess plans for dependencies, gaps, and continued business value. (ECO 2.9.2)
- Analyze the data collected. (ECO 2.9.3)
- Collect and analyze data to make informed project decisions. (ECO 2.9.4)
- Determine critical information requirements. (ECO 2.9.5)
- Plan and manage project compliance to business factors.
Deliverables, and Tools

Integration Management
- Many plans are built, maintained, and executed throughout a project.
- Project manager and others must assess and coordinate all plans and activities.
- A holistic, integrated view ties together, aligns efforts, and highlights how they depend on each other.
- An integrated view of all plans can identify and correct gaps or conflicts.
- A consolidation of the plans encapsulates the overall project plan and its intended business value.
Project Management Plan
A project management plan * is the document that describes how the project will be executed, monitored and controlled, and closed.
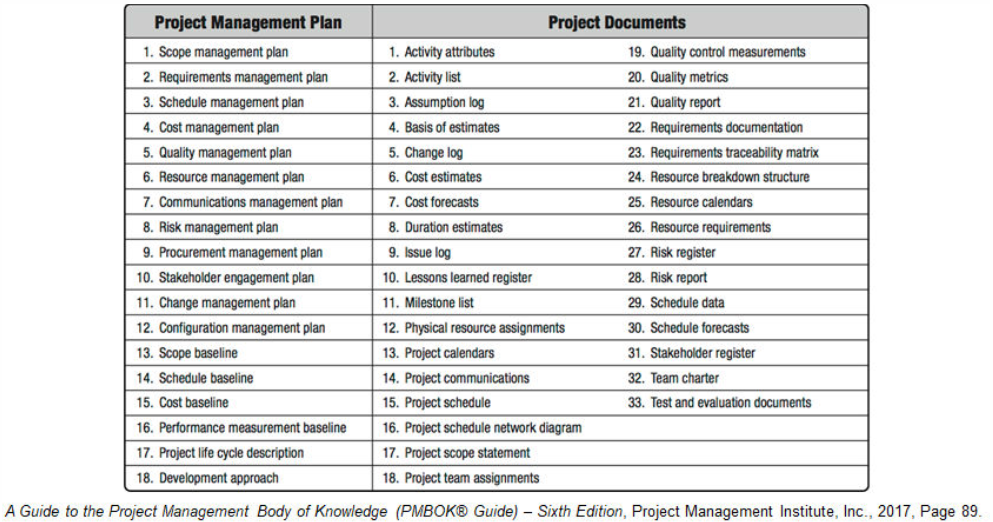
Project Management Plan Components
Baselines:
- Scope baseline
- Schedule baseline
- Cost baseline
- Performance measurement baseline
Life cycle
Project processes:
- Project management processes
- Level of implementation
- Tools and techniques
- How the selected processes will be used to manage
Work explanation
Agile project plan
Subsidiary plans:
- Scope management plan
- Requirements management plan
- Schedule management plan
- Cost management plan
- Quality management plan
- Resource management plan
- Communications management plan
- Risk management plan
- Procurement management plan
- Stakeholder engagement plan
- Configuration management plan
- Change management plan
- Compliance management plan
Project Management Plan Tools and Techniques
Expert judgment
Data gathering
- Brainstorming
- Checklists
- Focus groups
- Interviews
Interpersonal and team skills
- Conflict management
- Facilitation
- Meeting management
Meetings
Project Management Information System (PMIS)
A Project Management Information System (PMIS) * is an information system consisting of the tools and techniques used to gather, integrate, and disseminate the outputs of project management processes.
Enables quick and efficient scheduling because calculating is performed automatically.
PMIS example: Microsoft Project
Configuration Management Plan
The configuration management plan * is a component of the project management plan that describes how to identify and account for project artifacts under configuration control, and how to record and report changes to them.
The configuration management plan details the following:
- What work products need to be managed.
- How these products will be created, stored, revised, documented, and archived.
- The processes and the authorization levels for doing so.
- The naming schemes for different types of revisions (e.g., Rev 1 to Rev 2 versus Rev 1 to Rev 1.1, etc.).
- Discusses release management for products which will be released incrementally.
Change Management Plan
A change management plan * is a component of the project management plan that establishes the change control board or involvement level of the Product Owner, documents that extent of its authority, and describes how the change control system will be implemented.
A change management plan can answer the following questions:
- Who can propose a change?
- What exactly constitutes a change?
- What is the impact of the change on the project's objectives?
- What steps are necessary to evaluate the change request before approving or rejecting it?
- When a change request is approved, what project documents must be amended to record the actions necessary to effect the change?
- How will these actions be monitored to confirm that they have been completed satisfactorily?
Compliance Management Plan
Another important aspect of the planning process involves compliance goals and requirements.
Compliance with:
- Appropriate government regulations
- Corporate policies
- Product and project quality
- Project risk
Project Compliance Plan is a sub-plan of the project management plan.
Components include:
- Classify compliance categories
- Determine potential threats to compliance
- Analyze the consequences of noncompliance
- Determine necessary approach and action to address compliance needs
Guidelines to Develop a Project Management Plan
- Review the project charter for the high-level boundaries of the project.
- Review outputs from other processes.
- Review EEFs.
- Review OPAs.
- Use tools and techniques.
- Use facilitation techniques.
- Document the project management plan.
- Assess incremental delivery options.
Scrum of Scrums and SAFe
Scrum of Scrums (SoS)*: A technique to operate Scrum at scale for multiple teams working on the same product, coordinating discussions of progress on their interdependencies, and focusing on how to integrate the delivery of software, especially in areas of overlap.
Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe): A knowledge base of integrated patterns for enterprise-scale lean-agile development.
Guidelines to Determine Critical Information Requirements
- Review the project stakeholders identified for the project.
- Review and update the communication needs and expectations for each stakeholder.
- Determine the primary points in the project that have the most touchpoints or stakeholders affected.
- Evaluate those project points for the information contained.
- Assess whether that information is best communicated to stakeholders.
- Examine smaller points around the primary points to assess their value to stakeholders.
- Prioritize the points of information needs.
- Agree as a group or with the impacted stakeholders on a cutoff line between the most business critical information and those less critical.
- Set those at higher priorities to be critical information requirements.
- Review and update these requirements regularly.